Zoology related Pages:
- Zoology
- Animal Kingdom Classification
- Beginning of Life
- Animal Diversity
- Apiculture
- Fishery
- Capture Fisheries
- Culture Fishery
- Fish breeding
- Induced Breeding
- Composite Fish Culture
- Carp Disease
- Prawn Culture
- Brackish-Water Prawn Culture
- Sericulture
- Silkworm Diseases
- Mulberry Tree
- Cultured Pearls
- Poultry Farming
- Poultry Feed
- Rat Problem
- Rat Control
- Medical Zoology
- Life Cycle of Mosquito
- Roundworm
- Tapeworm
- Stem Borer
- Rice Bugs
- Protozoa
- Porifera
- Cindaria
- Ctenophora
- Nematoda
- Epithelial Tissue
- Types of Epithelial Tissue
- Connective Tissue
In the study of zoology there has a vital part of animal kingdom classification. Numerous living organisms are exist on the earth. Out of those organisms a large number of animals are there. All these animals are collectively formed the animal kingdom. Still today more than a million species of animal have been identified. Their structure, nature and life processes a full of diversified. Some of the animal organisms are living in water, some are on land and maximum of them are living in the air. In this way they occupy more or less all the media of the earth. Some of them act like an enemy to the human being but some other are acting like a friend. To realise and study this wide nature of animals the animal kingdom classification becomes very essential. The classification has been made on the basis of their resemblances and relationships.
What is classification?
Classification is defined as an orderly or ranking of organisms into groups or sit on the basis of their relationship.
What is the necessity of animal kingdom classification?
a) By classifying the organisms, they are divided into large as well as small groups so that one can easily get an idea about the groups and the individual type.
b) Scientific identification and naming of organisms is possible here.
c) Classification helps to understand the process of organic evolution.
Types of animal kingdom classification: -
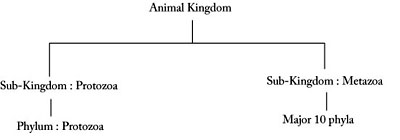
It has become a formidable task to classify the animal kingdom. Because, different scientists have been classified it differently. Some of the scientists classified the animal kingdom on the basis of the numbered of cells. On this basis the animal kingdom is classified image your sub-kingdoms, such as protozoa and metazoa. The sub- kingdom is again classified into one phylum which is also known as protozoa but metazoa is divided into many image your phyla. In this type of classification protozoan animals are called single celled organisms and metazoan are all multicellular animals.
Animal Kingdom (On the basis of number of cells)
Some scientists have made the animal kingdom classification on the basis of absence and presence of notochord into two groups, such as Non-chordata or Achordata and Chordata. The animals which have no notochord are placed in non –chordata group and the animals that possess the notochord in the body are placed under the group of chordate.
On the Basis of Absence and Presence of Notochord
The notochord in majority of chordates is subsequently replaced by vertebral columns, which are known as vertebrates. In the case of small number of chordates, the notochord is not being replaced by vertebral column rather notochord remains as a notochord, and they are regarded as protochordates. But in non-cordates, notochord and vertebral column both are absent.
On the Basis of Absence and presence of Vertebral Column
The vertebral column is absent in the invertebrates but presents in all animals of the vertebrate group.
For animal kingdom classification the modern zoologist have elevated some of the previously accepted classes to phylum status.  Many invertebrate animals have been searched out and many of them have now been placed in the new phyla yet their position in the animal kingdom remains n uncertainty. So the classification is becoming more and more complex day by day. By eliminating the complexity in modern animal kingdom classification, the animal kingdom is divided into few major bigger groups is known as phylum. Each phylum is divided into classes, each class into orders, each order into families, and family into genus. Each genus consist of one or more species and it is the smallest unit of classification.
Many invertebrate animals have been searched out and many of them have now been placed in the new phyla yet their position in the animal kingdom remains n uncertainty. So the classification is becoming more and more complex day by day. By eliminating the complexity in modern animal kingdom classification, the animal kingdom is divided into few major bigger groups is known as phylum. Each phylum is divided into classes, each class into orders, each order into families, and family into genus. Each genus consist of one or more species and it is the smallest unit of classification.